Guardium Insights - Online Installation
Installing Guardium Insights 3.0.x
This is my notes on installation of Guardium Insights 3.0.x on ROKS (OpenShift Cluster on IBM Cloud). This installation is interactive, no Ansible scripting is used in this case.
If any of the following steps fails, please consult the Installation Details at - See IBM Documentation on Guardium Insights 3.0.x Installation
This script covers installing Guardium Insight in an ROKS environment that has internet connectivity.</br> Refer to documentation for information on performing an air-gapped installation
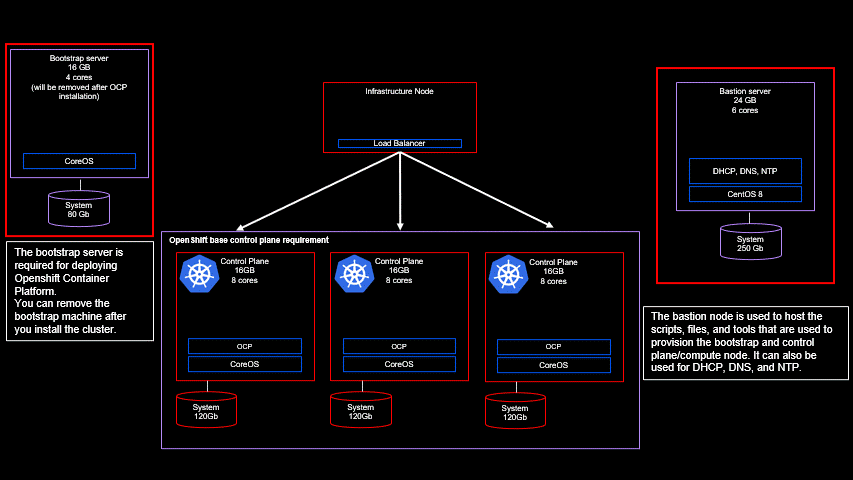
Hardware and Operating System requirements
Before beginning the installation of Guardium Insights, you will first need to provision a Redhat Openshift cluster.
For Guardium Insights version 3.0.x the version of Openshift needs to be v4.6.x.
View IBM documentation for hardware requirements for Guardium Insights
View IBM documentation for software requirements for Guardium Insights
I have used a very small cluster for testing:
ibmcloud oc cluster create --name my_gi_project --location DC13 --version 4.6.42_openshift --flavor b3c.16x64.encrypted --workers 3 --public-vlan 3112928-2939-fcr01a.dal13 --private-vlan 3112930-1788-bcr01a.dal13
Pre-deployment Environment Set Up
Workstation prerequisites
Ensure required CLI software installed
oc login <OCP endpoint> (Workstation must be logged in to the Openshift cluster
cloudctl >= 3.7.1 Download link
oc >= 4.4.6 Download link
kubectl >= 1.16 Download link
openssl 1.1.1, ssh-keygen, base64, cat, echo, grep, awk, rm, tr, cut
python --version (@ version 2.7+) with PyYAML installed
You must have cluster administrator privileges to run the setup scripts.
Set up storage
To Configure NFS with IBM Cloud File Storage (ibmc-file-gold-gid), run commands 1,2 and 3 on the link below.
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/cloud-paks/cp-data/3.0.1?topic=nsr-configuring-nfs-cloud-file-storage-gold-storage-class#aese-cfg-nfs-filegold
Install IBM Common Services
To install Guardium Insights, you will install Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform Version 4.6.x or Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform Version 4.7.x and IBM Cloud Pak foundational services Version 3.7.4 before adding Guardium Insights.
Doc reference: IBM Cloud Pak foundational services
- Log in to your OpenShift Cluster instance
example:oc login --token=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx --server=https://<your cluster address><br> - Set environment variables for IBM git repo user and password. Repo signon, namespace, and local directory for install files.
export CP_REPO_USER=cp export CP_REPO_PASS=<entitlement_key> export NAMESPACE=<guardium_insights_namespace, staging for example> export LOCAL_CASE_DIR=$HOME/guardium/insights/offline mkdir $LOCAL_CASE_DIRwhere:
is the entitlement key, as described in [Obtain your entitlement key](https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/guardium-insights/3.0.x?topic=installing-prepare-security-guardium-insights#install_prep_insights__entitlement_key).
is the namespace you chose in the above step, "staging" for example. - Obtain the Container Application Software for Enterprises (CASE) bundle:
- Specify the CASE version that is supported for the version of Guardium Insights that you are installing (see Container Application Software for Enterprises (CASE) and Operator version support). Git repo
For example, if you are installing Guardium Insights Version 3.0.1, you will specify the 2.0.1 bundle file:
export CASE_ARCHIVE=ibm-guardium-insights-2.0.1.tgz - Save the CASE bundle locally:
cloudctl case save \ --case https://github.com/IBM/cloud-pak/raw/master/repo/case/${CASE_ARCHIVE} \ --outputdir $LOCAL_CASE_DIR --tolerance 1
- Specify the CASE version that is supported for the version of Guardium Insights that you are installing (see Container Application Software for Enterprises (CASE) and Operator version support). Git repo
- Create namespace for common services, recommended name is
ibm-common-services :oc create namespace ibm-common-services - Install the IBM Common Services Catalog:
cloudctl case launch \ --case ${LOCAL_CASE_DIR}/${CASE_ARCHIVE} \ --namespace ibm-common-services \ --inventory ibmCommonServiceOperatorSetup \ --action install-catalog \ --tolerance 1 \ --args "--registry icr.io"check pod and catalog source status:
oc get pods -n openshift-marketplace oc get catalogsource -n openshift-marketplaceExample output: ``` NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE opencloud-operators-6czqp 1/1 Running 0 49s
NAME DISPLAY TYPE PUBLISHER AGE opencloud-operators IBMCS Operators grpc IBM 52s
6. Install IBM Common Services Operators:
#Set ICS_SIZE to medium if installing a GuardiumInsights size of values-xsmall or values-small #Set ICS_SIZE to large if installing a GuardiumInsights size of values-medium or higher $ export ICS_SIZE=<[medium|large]>
cloudctl case launch
–case ${LOCAL_CASE_DIR}/${CASE_ARCHIVE}
–namespace ibm-common-services
–inventory ibmCommonServiceOperatorSetup
–tolerance 1
–action install-operator
–args “–size ${ICS_SIZE}”
Confirm all common services pods are in "Running" or "Completed" status. This should take a while (10-20 minutes?). Note that pods may be in INIT status, make sure all have completed before proceeding:<br>
oc get pods -n ibm-common-services
7. Retrieve and export the IBM Common Services console credentials (required for Guardium Insights installation):
The default username to access the console is admin. You can retrieve the password for admin by issuing the following command:
export ICS_PASS=oc -n ibm-common-services get secret platform-auth-idp-credentials -o jsonpath='{.data.admin_password}' | base64 -d
export ICS_USER=admin
You can verify the password set correctly by echoing it.
echo $ICS_PASS
### Install IBM Guardium Insight
1. Define and create a namespace for your installation, for example "staging", and change context to itP
export NAMESPACE=staging oc create namespace ${NAMESPACE} oc project ${NAMESPACE}
2. Create Certificates as needed
* see steps on certificate creation.
3. Run the Guardium Insights pre-installation script:
create variable with DB nodes
export DB_NODES=10.73.241.145,10.73.241.152,10.73.241.167
* note no carriage returns in args
cloudctl case launch
–case ${LOCAL_CASE_DIR}/${CASE_ARCHIVE}
–namespace ${NAMESPACE}
–inventory install
–action pre-install
–tolerance 1
–args “-n ${NAMESPACE} -a ${ICS_USER} -p ${ICS_PASS} -h ${DB_NODES} -t false –ingress-keystore ~/training/guardium/insights/gi_keys/tls.crt –ingress-cert ~/training/guardium/insights/gi_keys/tls.key –ingress-ca ~/training/guardium/insights/gi_keys/ca.crt “
ALTERNATIVELY:
cloudctl case launch
–case ${LOCAL_CASE_DIR}/${CASE_ARCHIVE}
–namespace ${NAMESPACE}
–inventory install
–action pre-install
–tolerance 1
–args “-n ${NAMESPACE} -a ${ICS_USER} -p ${ICS_PASS} -h ${DB_NODES} -t false”
** note the assignments as follows
ingress-keystore = tls.crt
ingress-cert = tls.key
incress-ca = ca.crt
5. Install Guardium Insights catalogs
```
cloudctl case launch \
--case ${LOCAL_CASE_DIR}/${CASE_ARCHIVE} \
--namespace openshift-marketplace \
--inventory install \
--action install-catalog \
--tolerance 1
```
Check versions if this step gives problems. GI has specific compatibility with OCP versions.
```
oc -n ibm-common-services get csv
```
command will return the versions of common services.
Check that catalogs are installed:
```
> oc get pod -n openshift-marketplace
ibm-cloud-databases-redis-operator-catalog-ms97x 1/1 Running 0 12m
ibm-db2uoperator-catalog-k8pwc 1/1 Running 0 13m
```
6. Install operators for Guardium Insight
Pull image from registry and install
cloudctl case launch \
--case ${LOCAL_CASE_DIR}/${CASE_ARCHIVE} \
--namespace ${NAMESPACE} \
--inventory install \
--action install-operator \
--tolerance 1 \
--args "--registry cp.icr.io --user ${CP_REPO_USER} --pass ${CP_REPO_PASS} --secret ibm-entitlement-key" ``` verify install: ``` oc get pods ``` Result should show the relevant DB pods, for example: ``` NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE db2u-operator-manager-66698df54c-wsl9x 1/1 Running 0 15h guardiuminsights-controller-manager-599769cd86-h7d9p 1/1 Running 0 15h ibm-cloud-databases-redis-operator-69fb7f4596-gp8km 1/1 Running 0 15h mongodb-kubernetes-operator-6c5dccf4f4-9xqjn 1/1 Running 0 15h ``` ## Deploy Guardium Insights [IBM documentation](https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/guardium-insights/3.0.x?topic=installing-deploying-security-guardium-insights) <br>
- Create mygi.yaml file as described in documentation
apiVersion: gi.ds.isc.ibm.com/v1 kind: GuardiumInsights metadata: #name: This must be 10 or less characters name: staging spec: version: 3.0.1 license: accept: true licenseType: L-TESX-C24QW3 guardiumInsightsGlobal: dev: "false" licenseAccept: true fsGroupGid: 1001 # Guardium Insights template size can be defined as below using the size parameter size: values-small image: #insightsPullSecret needs to be set to the following developer/QA workflow insightsPullSecret: ibm-entitlement-key #repository needs to be set to the following developer/QA workflow repository: cp.icr.io/cp/ibm-guardium-insights insights: ingress: #hostName: Change this, ex: staging.apps.gi-devops-ocp46-41.cp.fyre.ibm.com hostName: staging.mycluster-dal13-b3-925660-564f2d47ac91e8f35bb41f7dc2ee4fde-0000.us-south.containers.appdomain.cloud #domainName: Change this domainName: mycluster-dal13-b3-925660-564f2d47ac91e8f35bb41f7dc2ee4fde-0000.us-south.containers.appdomain.cloud #storageClassName: Change this to a ReadWriteMany StorageClass!!! ics: namespace: ibm-common-services registry: common-service storageClassName: ibmc-file-gold-gid - Apply the yaml file
create the instance:
oc create -f mygi.yaml - Check the status
instance creation status:
oc get guardiuminsightsThis will print out the name and status of the guardiuminsights deployment. Status will change through “Running reconciliation” to “Starting to Reconcile” and other status. can take several minutes.
If you need to roll it back, useoc delete -f gi_config.yamlCertificates
Create a subdirectory in the installation folder to create and store keys used during this installation and create variable with your selected domain name (FQDN).
export GI_KEYS=$LOCAL_CASE_DIR/gi_keys mkdir ${GI_KEYS} cd ${GI_KEYS} export DOMAIN="gitest.jaydee.xyz"create certificates in this directory
cat <<EOF > openssl.cfg [ req ] distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name [ req_distinguished_name ] commonName = $DOMAIN commonName_max = 64 [ v3_ca ] basicConstraints = critical,CA:TRUE subjectKeyIdentifier = hash authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer:always EOFCreate keys
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 4096 openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ca.key -sha256 -days 825 \ -config openssl.cfg -extensions v3_ca \ -subj "$SUBJ" -out ca.crt
Assign domain:
export DOMAIN="gitest.jaydee.xyz"
cat > openssl.cfg <<EOF
[req]
req_extensions = req_ext
x509_extensions = usr_cert
distinguished_name = req_name
[ req_name ]
commonName = $DOMAIN
[ usr_cert ]
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
nsCertType = server
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid,issuer
subjectAltName = DNS:$DOMAIN
[ req_ext ]
subjectAltName = DNS:$DOMAIN
EOF
You must provide a TLS certificate for the platform Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). See IBM Docs for details on Domain Name and TLS Cert
Domain name requirements
If your Cloud Pak for Security platform is installed on IBM Cloud® or Amazon Web Services (AWS), the FQDN of the Red Hat® OpenShift® Container Platform cluster will be used with the TLS certificate for the platform FQDN. In this case, it is optional to create an FQDN.
For installation, Cloud Pak for Security requires a server private key and server certificate that use keys that are signed by a trusted certificate authority (CA).
An extra authority certificate is required if the provided server keys are signed by a non-trusted authority.
If you need to generate a signing CA certificate, you can use the following example. The SUBJ environment variable is the name of the CA for which the certificate is generated, for example “/CN=My CA”.
cd ~ mkdir cp4s_keys cd cp4s_keys
export SUBJ=”/CN=«Enter CA subject»”
cat «EOF > openssl.cfg [ req ] distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name [ req_distinguished_name ] commonName = Common Name (for example, fully qualified host name) commonName_max = 64 [ v3_ca ] basicConstraints = critical,CA:TRUE subjectKeyIdentifier = hash authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer:always EOF
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 4096
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ca.key -sha256 -days 825 -config openssl.cfg -extensions v3_ca -subj “$SUBJ” -out ca.crt As a result of running the above code, you should see three files in directory “~/cp4s_keys” i.e. ca.key , ca.crt and openssl.cfg. These generated filescontaining the key and certificate for the CA.
To generate the server certificates, you can use the following example. The ca.key and ca.crt files can contain the key and certificate of the signing CA that you generated from the previous example, or your own key model. The DOMAIN environment variable is the name of domain for which the certificate is generated. For wildcard certificates, the value must start with ‘*.’
Create the OpenSSL configuration.
export DOMAIN=”«Enter domain here»”
cat > openssl.cfg «EOF [req] req_extensions = req_ext x509_extensions = usr_cert distinguished_name = req_name [ req_name ] commonName = $DOMAIN [ usr_cert ] basicConstraints=CA:FALSE nsCertType = server keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth subjectKeyIdentifier = hash authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid,issuer subjectAltName = DNS:$DOMAIN [ req_ext ] subjectAltName = DNS:$DOMAIN EOF Generate the certificate.
subj=”/CN=$DOMAIN”
openssl req -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout tls.key -outform PEM
-out tls.csr -subj “$subj” -config openssl.cfg
openssl x509 -req -sha256 -in tls.csr
-out tls.crt.tmp
-CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key
-CAcreateserial -CAserial ca.serial
-days 398 -extensions usr_cert -extfile openssl.cfg
cat tls.crt.tmp ca.crt > tls.crt The result of using this example is that tls.key and tls.crt files are generated, containing the server key and certificate for the domain. The following certificates and key are generated by the example: tls.crt, tls.key, ca.crt. Sequentially, these certificates map to the following installation parameters: cp4sdomainCertificatePath, cp4sdomainCertificateKeyPath, cp4scustomcaFilepath. TLS Certificate parameters in installation
Air-gapped info
Set up a private Docker registry that is access from both your local machine adn the airgapped cluster, then set these environment variables:
export LOCAL_REGISTRY_HOST=<host IP or FQDN:Listening port>
export LOCAL_REGISTRY_USER=<Username for your private registry>
export LOCAL_REGISTRY_PASS=<Password for your private registry>
export CP_REPO_USER=<Your Username to cp.icr.io>
export CP_REPO_PASS=<Your Password / Entitlement Key to cp.icr.io>
export NAMESPACE=<your chosen namespace>
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/guardium-insights/3.0.x?topic=pisgi-prepare-your-environment-offline-air-gap-installation-guardium-insights
Then proceed with the steps to save the CASE bundle locally and proceed with install